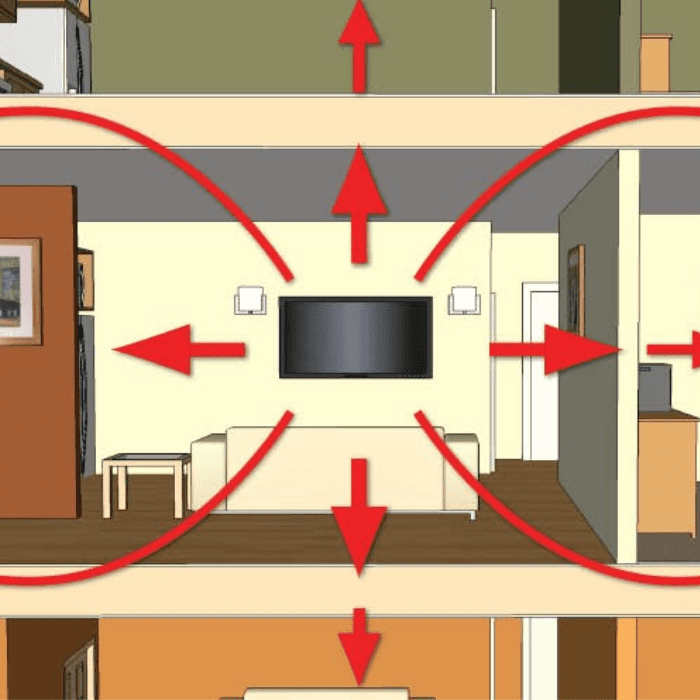
Understanding Sound Insulation
Understanding Sound Insulation and How Soundproofing Works for Airborne and Impact Noise Reduction
Sound insulation is essential to modern construction, ensuring comfort and privacy in homes, offices, and commercial spaces. However, many people don’t fully understand how sound travels or how soundproofing solutions work to block different types of noise. In this article, we’ll dive into the science of sound insulation and how it effectively combats airborne and impact noise.
What Is Sound Insulation?
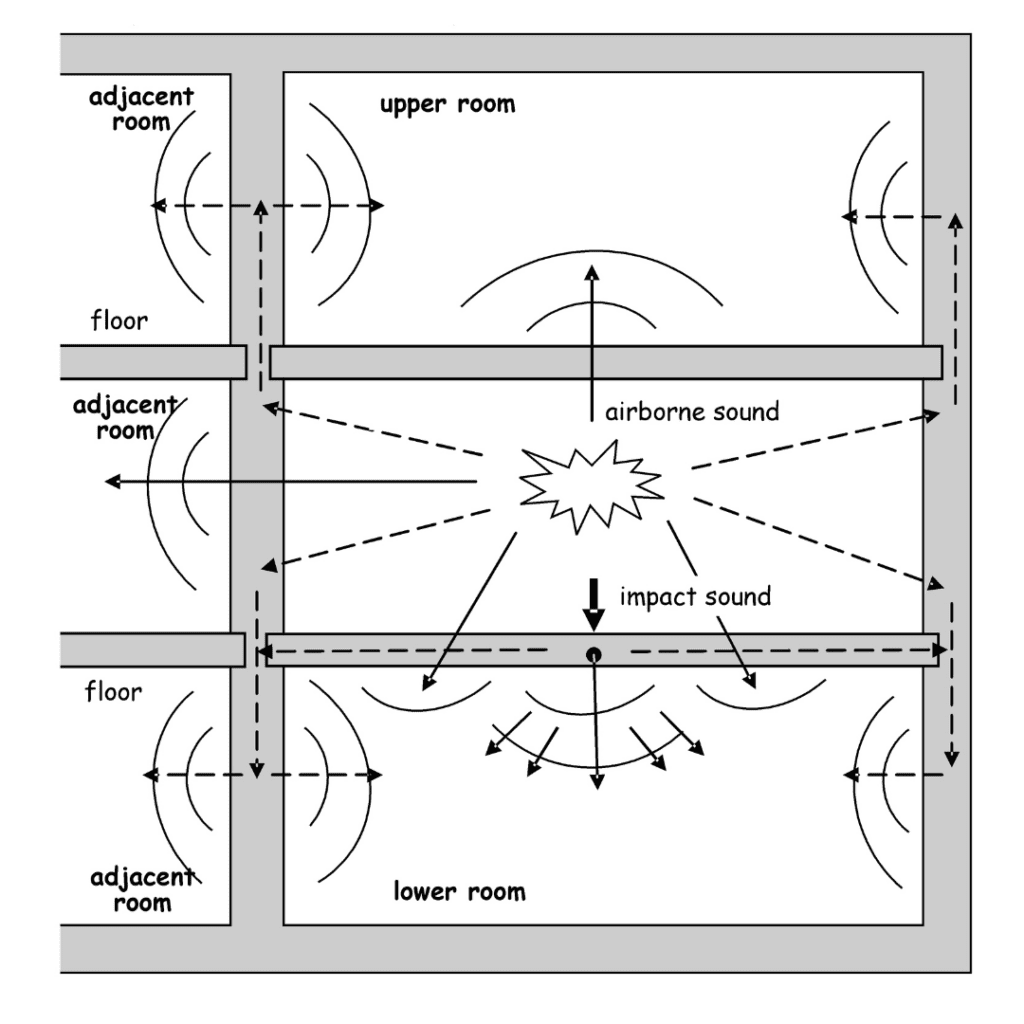
Sound insulation refers to the materials and construction techniques that reduce sound transmission between different spaces. It helps keep noise from travelling through walls, ceilings, floors, and windows, ensuring that sound stays where it’s supposed to be. Sound insulation aims to reduce two primary types of noise: airborne noise and impact noise.
Airborne Noise: What It Is and How to Control It
Airborne noise is a sound that travels through the air. Common sources of airborne noise include:
- Music or TV playing in another room
- Conversations
- Traffic outside a building
- Voices from adjacent apartments
Airborne noise enters a room through gaps, cracks, or porous surfaces in walls, ceilings, and windows. To block airborne noise, you need materials that add mass and density to the surfaces that sound waves pass through. Here are some key solutions for reducing airborne noise:
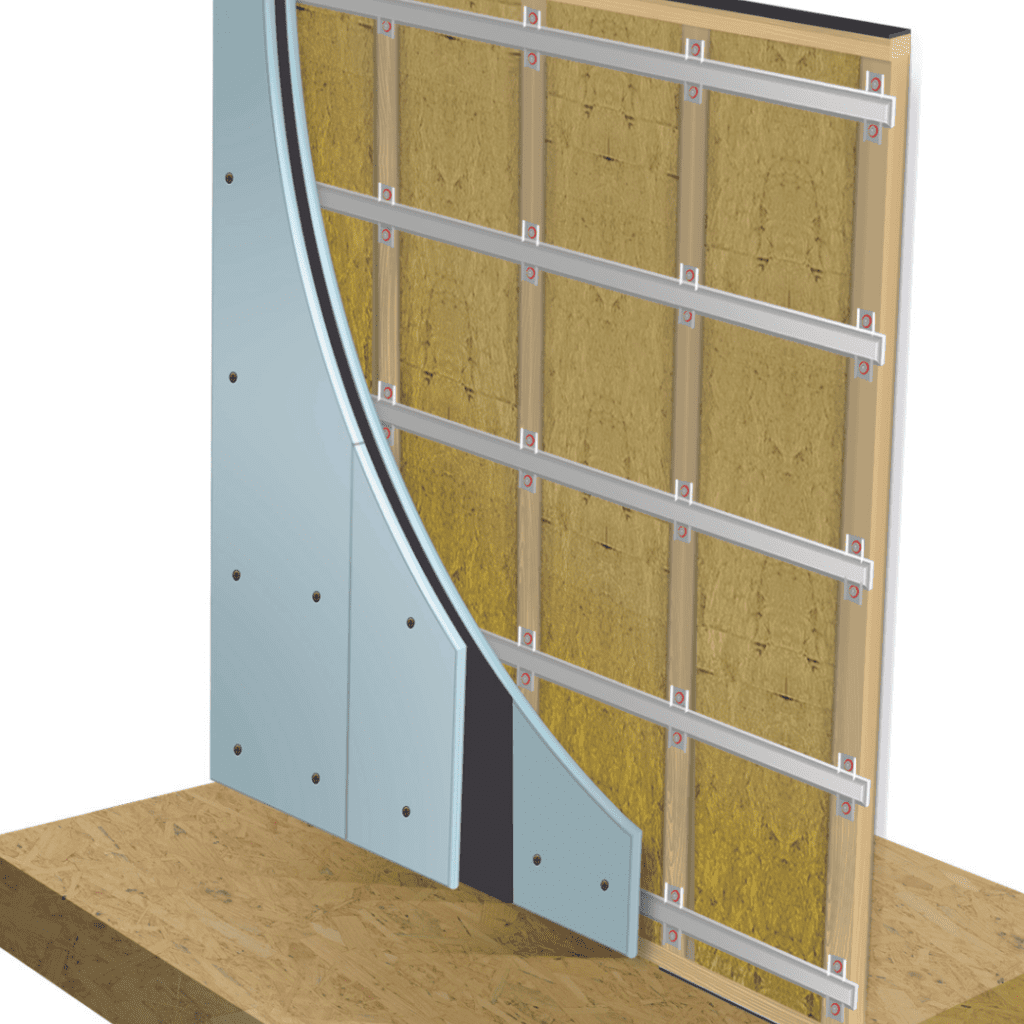
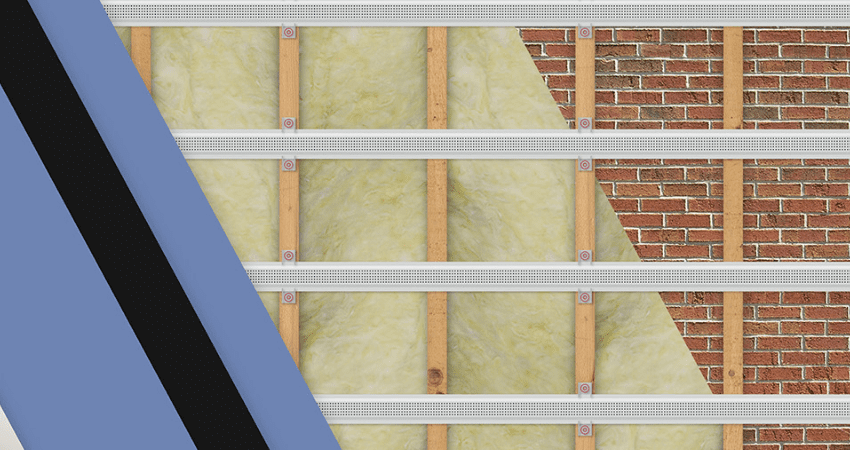
1. Soundproofing Walls
- Mass-loaded vinyl (MLV): This dense material is excellent for adding mass to walls and blocking sound waves from passing through.
- Soundproof panels: Installing a soundproof panel creates a heavier, more sound-resistant barrier.
- Acoustic Insulation: Soundproof insulation, such as fibreglass or rock wool, helps fill the cavity within stud walls, absorbing sound energy before it passes through.
- Decoupling sound isolation clips: Sound isolation clips reduce vibration through the wall which transfers the sound.
2. Sealing Gaps and Cracks
- Use acoustic caulk to seal gaps around windows, doors, and wall joints. Even small gaps can leak a significant amount of sound into a room.
- Weatherstripping doors and windows will also help reduce noise from outside.
3. Soundproof Doors and Windows
- Consider upgrading to solid-core doors, which provide better sound insulation than hollow-core doors.
- Installing double or triple-glazed windows with an air gap between the panes also reduces airborne noise transmission.
Soundproofing Walls
Please look at our wall soundproofing product range, which includes soundproof panels, complete acoustic wall soundproofing systems and all the essential sound insulation materials you will need to restore quiet in your home.
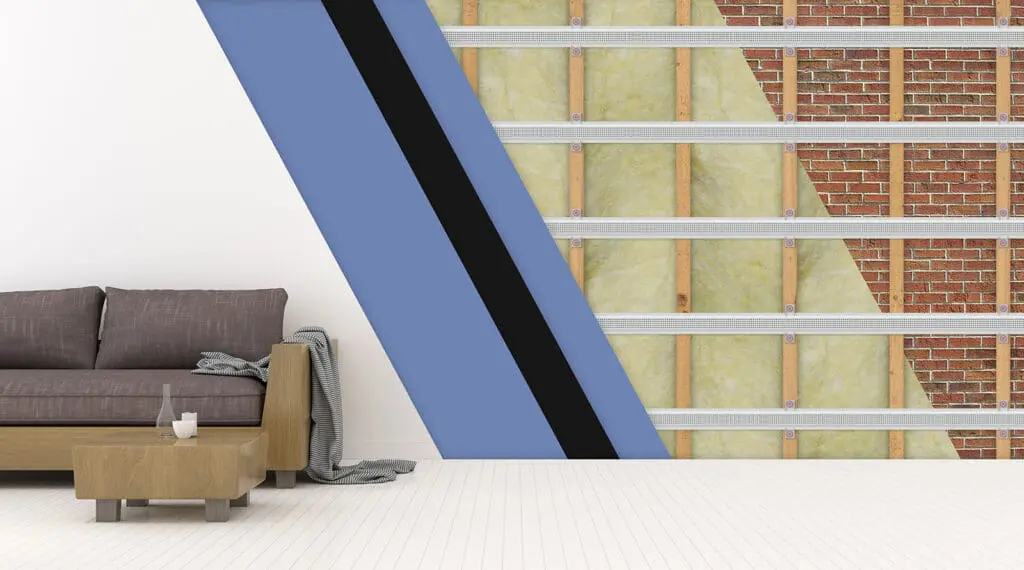

Impact Noise: What It Is and How to Control It
Impact noise is sound caused by physical impacts on a surface, such as:
- Footsteps on a floor above
- Objects dropping on a hard floor
- Moving furniture
Impact noise can be particularly troublesome in multi-story buildings or homes with hard flooring. Unlike airborne noise, this type of noise doesn’t travel through the air but rather through the structure itself, such as floors, ceilings, or walls.
To reduce impact noise, the key strategy is introducing materials that absorb shock and vibrations before travelling through the structure. Here are some ways to control impact noise:
1. Soundproofing Floors
- Acoustic Underlay: Installing acoustic underlay beneath hard flooring materials (like wood or tile) can absorb the impact from footsteps and dropped objects, preventing noise from travelling to rooms below.
- Carpet and Padding: Using thick carpeting with high-quality underpadding is an effective way to absorb impact noise.
2. Floating Floors
- A floating floor is a decoupled system where the subfloor is isolated and has no direct fixing into the floor joist. Adding a layer of cushioning material, such as resilient channels or rubber mats, removes the floor from the rest of the structure, significantly reducing impact sound.
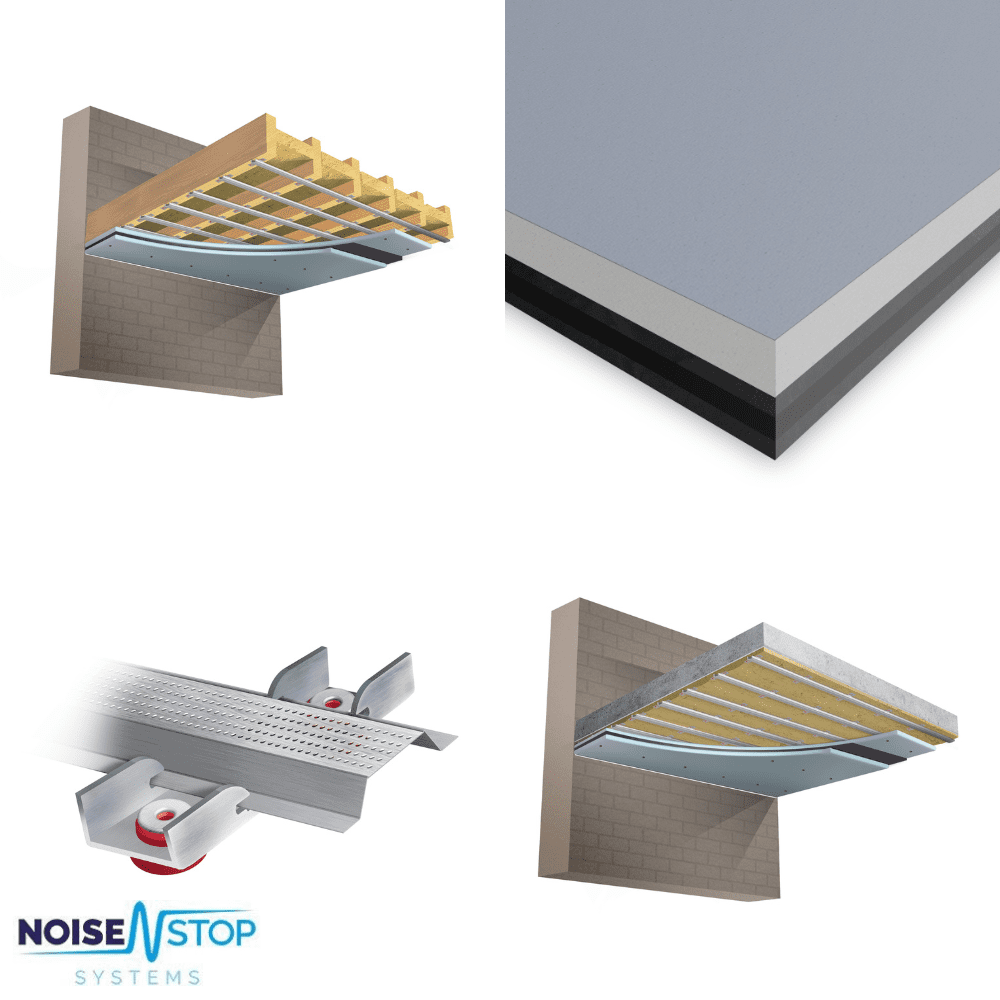
3. Ceiling Treatments
- Suspended Ceilings: Adding a suspended ceiling or a drop ceiling beneath the original can create an additional separation layer, absorbing the sound before it reaches the space below.
- Resilient Channels and isolation clips Isolate the existing ceiling structure from the new acoustic ceiling by absorbing sounds that vibrate through it.
Key Concepts: Decoupling, Mass, and Absorption
Effective soundproofing often involves three main principles:
- Decoupling: Involves separating structures (like walls or ceilings) to prevent sound from travelling directly through them. Techniques like using sound isolation decoupling clips or creating a floating floor are examples of decoupling.
- Adding Mass: Sound waves lose energy as they pass through dense materials. Adding mass to walls, floors, or ceilings (e.g., through layers of acoustic insulation and soundproof panels) helps block airborne sound.
- Absorption: Materials like acoustic insulation absorb sound energy, converting it into heat and preventing it from passing through walls, floors, and ceilings.
Combining Solutions for Comprehensive Soundproofing
To effectively combat both airborne and impact noise, it’s essential to combine different soundproofing methods:
- For airborne noise: Focus on adding mass to walls, ceilings, and doors, sealing gaps, and using soundproof windows.
- For impact noise: Treat floors with acoustic underlay and consider decoupling floors and ceilings.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between airborne and impact noise—and the best ways to control each—will help you choose the right soundproofing materials and methods for your space. By incorporating mass, decoupling, and absorption, you can significantly reduce the transmission of both types of noise, creating a quieter, more peaceful environment.
This guide provides a solid foundation for tackling noise issues in homes, apartments, studios, or commercial spaces. Investing in the proper soundproofing techniques makes all the difference for comfort and privacy.
Soundproofing posts
Categories
46 articles

Top 3 Recommended Solutions for Soundproofing Walls

How To Soundproof Floors

Soundproofing Floors FAQs

How to Soundproof a Party Wall
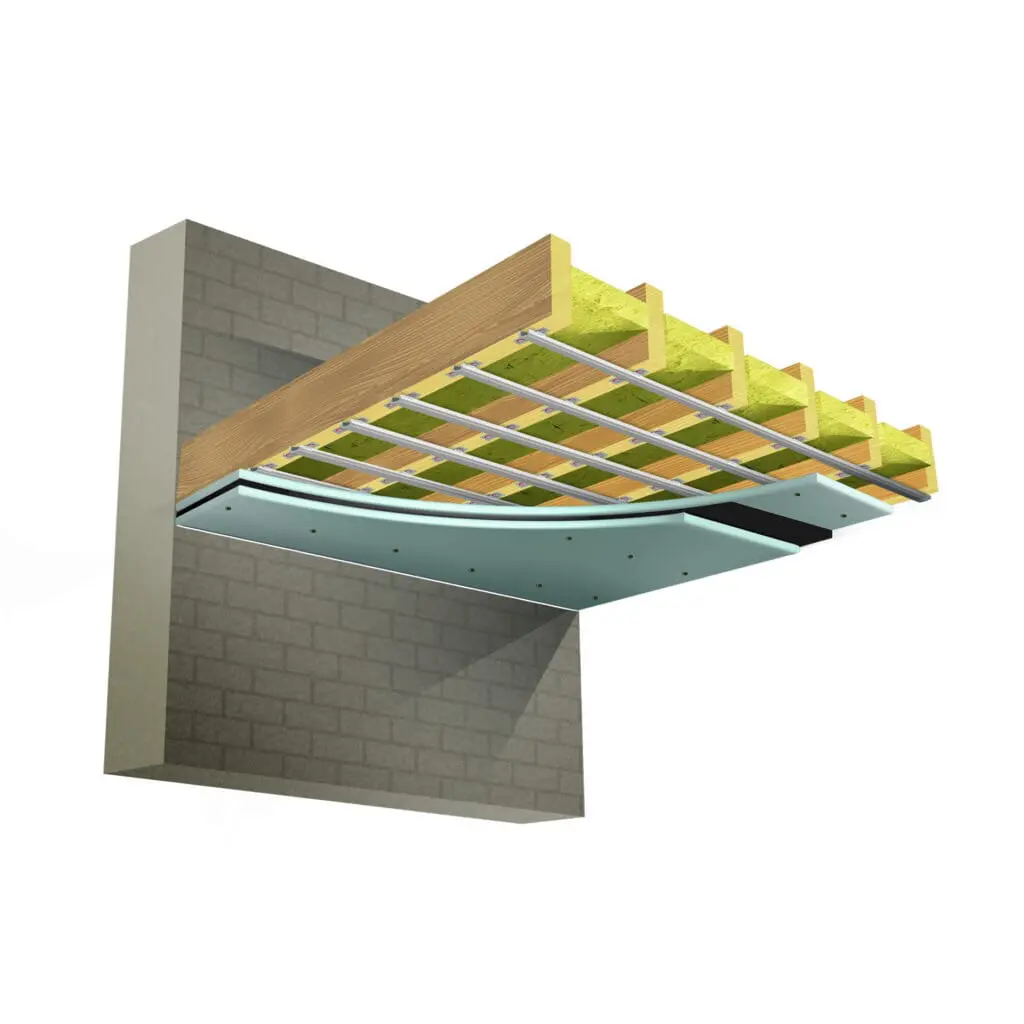
How to Soundproof a Ceiling
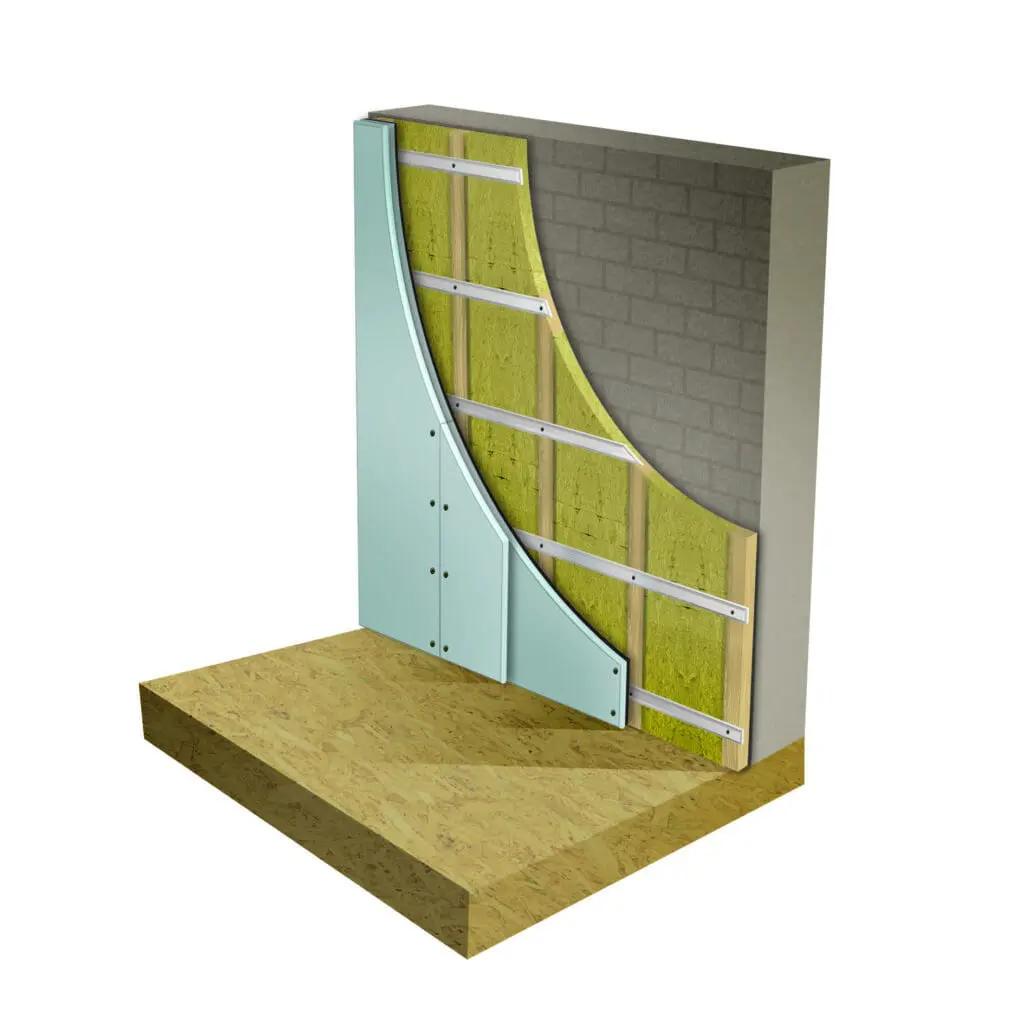
How To Soundproof Walls
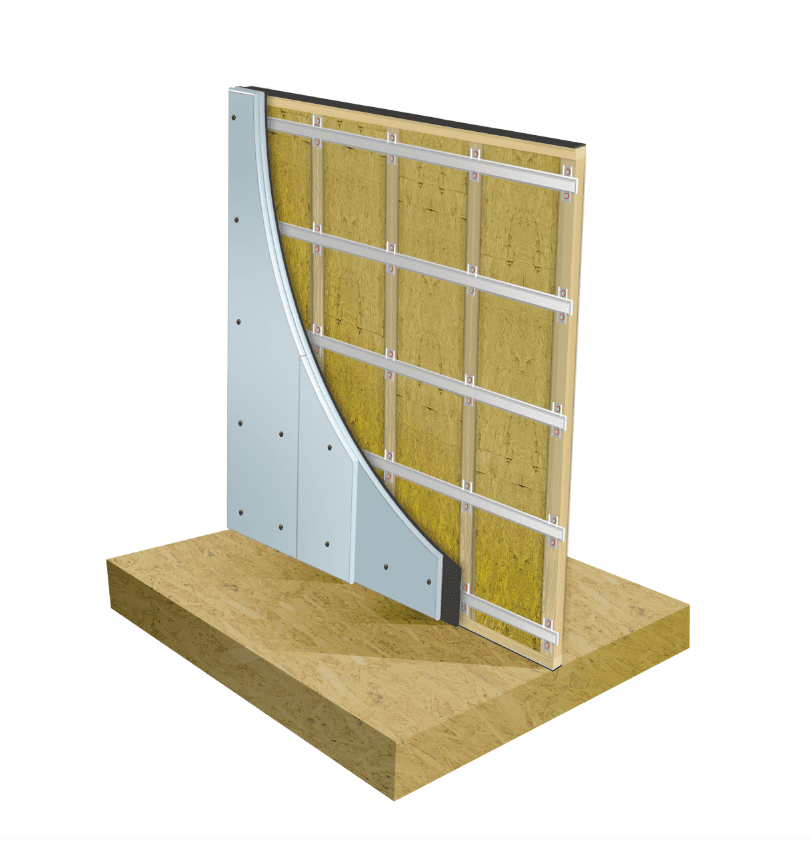
How To Soundproof a Stud Wall

Best Way to Sound Insulate a Wall

Best Sound Insulation For Walls

How to Soundproof a Room for a Home Cinema

Meeting Part E Building Regulations When Converting a Property into Separate Dwellings
What is the difference between airborne and impact noise?

What are the Best Soundproof Underlays?
Wall Sound Insulation

Best Soundproofing Products 2025
Soundproofing Materials for Walls
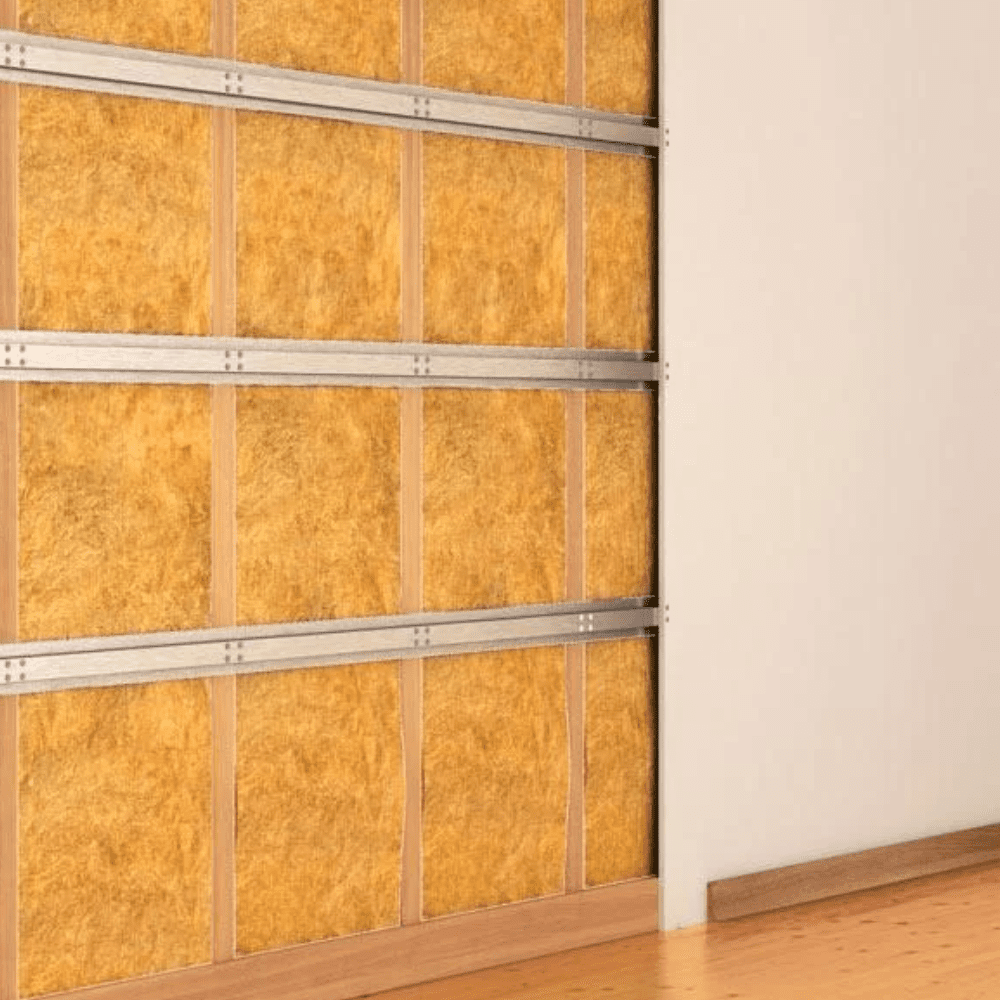

Understanding Sound Insulation

Guide To Soundproofing Your Home
Soundproofing Materials for Ceilings
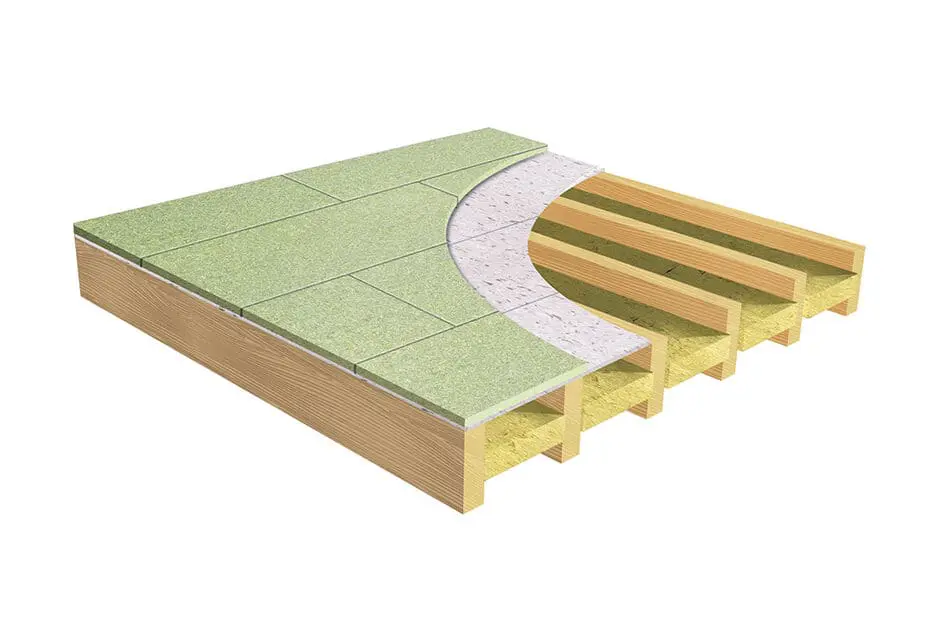
Part E Acoustic Solution for Timber Joist Separating Floors: Using Noisedeck 32, Insulation, and Soundbreaker Bars
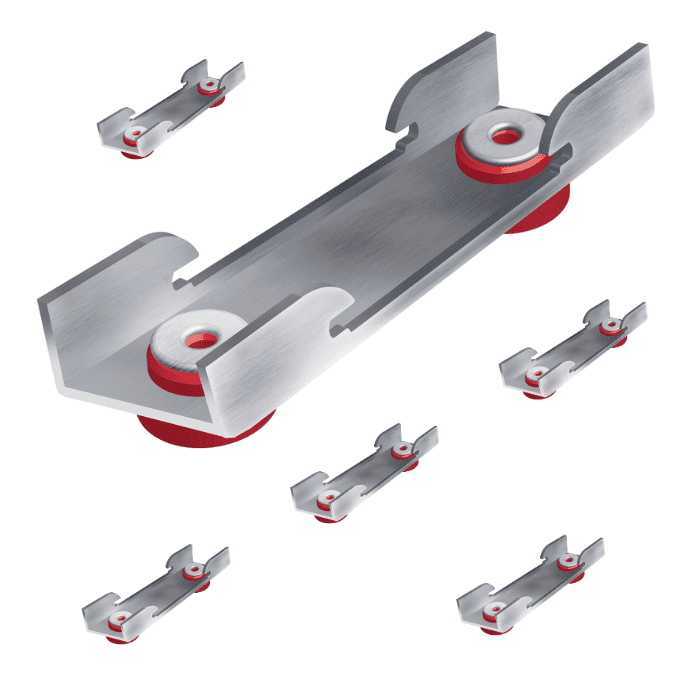
AcoustiClip Acoustic Wall Systems

Acoustic Sound Insulation Guide

Soundproof Insulation vs. Acoustic Insulation: Understanding the Difference